Spherical harmonics example¶
Plot spherical harmonics on the surface of the sphere, as well as a 3D polar plot.
This example requires scipy.
In this example we use the mlab’s mesh function:
mayavi.mlab.mesh().
For plotting surfaces this is a very versatile function. The surfaces can
be defined as functions of a 2D grid.
For each spherical harmonic, we plot its value on the surface of a sphere, and then in polar. The polar plot is simply obtained by varying the radius of the previous sphere.
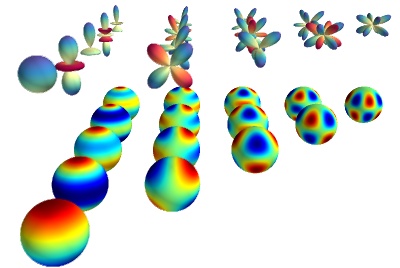
Python source code: spherical_harmonics.py
# Author: Gael Varoquaux <gael.varoquaux@normalesup.org>
# Copyright (c) 2008, Enthought, Inc.
# License: BSD Style.
from mayavi import mlab
import numpy as np
from scipy.special import sph_harm
# Create a sphere
r = 0.3
pi = np.pi
cos = np.cos
sin = np.sin
phi, theta = np.mgrid[0:pi:101j, 0:2 * pi:101j]
x = r * sin(phi) * cos(theta)
y = r * sin(phi) * sin(theta)
z = r * cos(phi)
mlab.figure(1, bgcolor=(1, 1, 1), fgcolor=(0, 0, 0), size=(400, 300))
mlab.clf()
# Represent spherical harmonics on the surface of the sphere
for n in range(1, 6):
for m in range(n):
s = sph_harm(m, n, theta, phi).real
mlab.mesh(x - m, y - n, z, scalars=s, colormap='jet')
s[s < 0] *= 0.97
s /= s.max()
mlab.mesh(s * x - m, s * y - n, s * z + 1.3,
scalars=s, colormap='Spectral')
mlab.view(90, 70, 6.2, (-1.3, -2.9, 0.25))
mlab.show()
